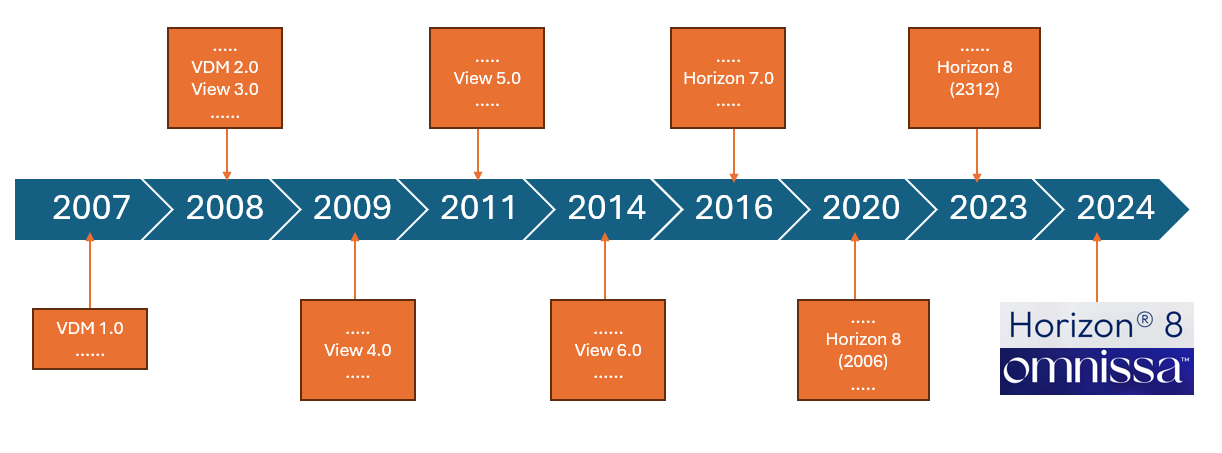
The exit of EUC services from Broadcom (after the acquisition of VMware by the US giant) has brought a situation of uncertainty for all those who have been appreciating for years the features of the VDI/Applications published with Horizon and all the products of the EUC ecosystem that were from VMware.
The birth of Omnissa (effective from the beginning of July) bodes well for the future (more information in this post of mine from a few weeks ago).
Of the many synergies that were natural when vSphere and Horizon were children of the same mother, the first uncertainty was the licensing issue.
VMware gave the possibility, once a specific Horizon license was purchased, to have the vSphere virtualization infrastructure licenses, practically a solution ready to be only implemented. (I remind you that Horizon also goes on other Hypervisors… obviously exploits 10% of the potential… on this issue. I expect news from Omnissa since vSphere and Horizon are no longer brothers). The only limitation of the vSphere license included in Horizon was the need to run on the vSphere platform, licensed with Horizon, only VDI environments and the servers necessary for operation (Connection Server ,,, App Volumes Manager etc ..)
Now that vSphere and Horizon no longer have the same mother, what happens to these licenses? Will I still be able to buy a bundle with Horizon and vSphere together?
This link explains that the best of the matter:
Setting the record straight: EUC to continue to offer Horizon with vSphere and vSAN (omnissa.com)
Where it is indicated that there will be a collaboration between Omnissa and Broadcom to allow the presence of a bundle with Horizon and vSphere.

So it is still possible to purchase one of the following licenses:
- Horizon Enterprise term
- Horizon Universal,
- Horizon Enterprise Plus
- Horizon Standard Plus
- Horizon Apps Universal
What is the name of the vSphere package included in Horizon Solutions?
VMware vSphere Foundation for VDI (VVF for VDI)
What does it include?
• vSphere Enterprise Plus
• vCenter Standard
• vSAN Enterprise (100 GB) (licensed per Core)
So how much space have I included in vSAN?
Well, the game is quite simple: for each core of my vSphere cluster on which I host VDI and on which I have the VVF for VDI licenses, just multiply 100GB by the number of CORES. (there are no restrictions on the number of cores)
Let’s focus on the vSAN Enterprise license… what difference do we have from the previous Bundle?
- vSAN Enterprise includes the same features as vSAN Advanced plus all those of vSAN Enterprise which are:
- Data-at-rest and data-intransit encryption
- File services
- VMware HCI Mesh™2
In this link more information: